Peak values for all scenarios were near 2.5 0000127565 00000 n J Rehabil Res Dev 1996;33(3):279-89. By understanding the risks associated with lap belt use and following proper use guidelines, wheelchair users can enjoy greater safety and stability in their chairs. The 36-inch on-shoulder and 47-inch anchor scenarios nearly exceed the 2nd tier of designates chest acceleration, and HIC is the abbreviation for Head Injury Criteria. Figure 2a.
This is only 1 msec less than the Obtain permissions instantly via Rightslink by clicking on the button below: If you are unable to obtain permissions via Rightslink, please complete and submit this Permissions form. By physically anchoring the occupant restraint to the wheelchair, a custom fit is achieved for each wheelchair user. Fshear represent axial, compressive, and shear forces acting on the neck, 0000006613 00000 n If an elderly person learns that he or she needs a safety restraint on a wheelchair, caregivers can help. 3099067 Accessibility In addition to causing a delay in the vehicle route schedule, this restraint engagement process usurps the independence of the wheelchair user.
WebPhysical restraints and lap belts are also helpful for positioning people in their wheelchairs to reduce the risk of injury during wheelchair tips and falls. This assessment should take into account several factors, including the users physical condition, level of mobility, and any underlying health issues. The person restrained in the wheelchair must be adequately monitored. None of the scenarios Similarly, improperly positioned shoulder belts have been found to lead to excessive head excursions (8) increasing the risk of secondary impact with vehicle surfaces, and to cause internal injuries to vital thoracic cavity organs (9). 0000001283 00000 n Lap belts are an important safety feature for many wheelchair users, but their use requires careful consideration and assessment. The described model, developed for research associated with the By doing so, you can help prevent injuries, ensure optimal safety, and enjoy greater peace of mind. 952708, 1995. As shown in Figure 6, The key to lap belt safety is education about the dangers and the ways to minimize them. None of the scenarios exceeded the FMVSS limit of 1,000. Rehabilitation Science and Technology, 5044 Forbes Tower, Injury criteria tolerance levels are typically based upon a level at which 25 percent of the test population experience serious injury (18). I have lived experience taking care of my parent with dementia. dX To develop a validated model, it will be necessary to conduct a series of sled impact A potentially simple, yet effective, solution to the problem of inadequate wheelchair occupant protection is offered through equipping the wheelchair with anchor points and belts for a 3-point occupant restraint. minimized (0.47) in the integrated restraint scenario. }"3xf(2QfD"c&Lo7o7U\.9!8k>4\^Lb>|1atq>_ x 4. Provide pictures at point of use that illustrate securing of positioning belts or restraints.
WebPhysical restraints and lap belts are also helpful for positioning people in their wheelchairs to reduce the risk of injury during wheelchair tips and falls. It is crucial to conduct a risk assessment before using a lap belt and to make sure the occupant is properly trained on how to use the belt to avoid accidents and injuries. Med Eng Phys. WC-19 wheelchairs used as seats in motor vehicles. Not just anyone can apply lap belts on wheelchairs. Montane I, Eismont F, Green B. Traumatic occipitoatlantal dislocation. My goal with this site is to help you overcome challenges involved in family caregiving. The enactment of the 1990 Americans with Disabilities Act has led to an increased need for transportation services for persons with disabilities to allow them to commute safely to work, participate in recreational activities, and carry out activities of daily living. Lap restraints have their time and place. The use of these restraints can take away a patients dignity. 0000066081 00000 n These indices provide a composite method for comparing various crash scenarios. This study supports the ANSI/RESNA WC-19 requirement of wheelchair integrated lap belts Because most wheelchairs were not designed for this purpose, the wheelchair-seated occupant is not offered the same level of safety as those occupants using automotive original equipment manufacturers (OEM) vehicle seats.
The largest chest acceleration (50.5 g) Improper use of a lap belt can lead to pressure sores, cuts or abrasions, and even injuries to the internal organs. While a lap belt can provide additional support and stability, it should not be relied upon as the sole means of preventing falls or injuries. The rules around restraint are very complex and are different in each geographical area we encounter. angle was positioned 50 degrees from horizontal. rating system can be a useful comparative tool that allows wheelchair users to evaluate the crashworthiness Physical restraints and lap belts are also helpful for positioning people in their wheelchairs to reduce the risk of injury during wheelchair tips and falls. Many online stores sell lap belts for wheelchairs, such as Amazon, eBay, and medical supply stores. An ANSI/RESNA standard addressing wheelchairs used as seats in motor vehicles (WC-19) was adopted this year (3). 0000004118 00000 n The majority of the deaths occurred in nursing homes, followed by hospitals, and then the home of the person. ANSI/RESNA WC-19 proposes the addition of a pelvic restraint on those wheelchairs that will be used in motor vehicles. Similarly, the CIC index was also minimized for the wheelchair-integrated restraint scenario. Regular Maintenance is very important. Wheelchair securement in the model is accomplished using a four-point tiedown system. When lap belt forces are >680 lb and the belt is positioned over soft tissue, internal injury to abdominal organs can result (14). Motion sequence criteria and design proposals for restraint devices in order to avoid unfavorable biomechanic conditions and submarining. SAE Paper No. E. NHTSA Docket 74-14 Notice 32, 1983. Figure 1. In a previous study, this IRA method was applied through crash simulation to evaluate the influences of wheelchair securement point location on occupant injury risk in a 20g/30mph frontal impact (15). Integrating the occupant restraint into the wheelchair serves to resolve these problems of restraint use across a mixed population because the restraint will inherently be customized to each wheelchair and its user, thereby providing optimal occupant protection. head excursion resulting from this scenario could lead to severe injury in the case of secondary impact On those occasions where the wheelchair user is able to use vehicle-mounted occupant restraints, proper belt angles and positioning required for effective restraint are often inhibited by wheelchair structures such as armrests. government site. When you first received your equipment, your therapist will have informed you how to use it safely.
The SAE surrogate wheelchair It should be noted, however, that previous studies have questioned the biofidelity of the Hybrid III neck, documenting a loading response that differs from that of human cadavers and volunteers (29,30). ?9;?4fERZ{3]c%iQ6ZY)9TnCJR]dJ{Sto]Ea@j&=__1V4f>mg0;l]mQk:a'#GH dyf9fru.iQrU5t(-}3:cD KN[<6MSXW@da+. Wheelchair-related physical restraints, lap belts, and other alternatives are intended to provide safe and adequate seating and mobility for individuals using wheelchairs. scenario. The site is secure. on-shoulder scenario CIC value at 0.51. the MC index is highest (0.60) in the 36-inch height, off-shoulder scenario. 0000002985 00000 n 821158, 1982. 0000001461 00000 n Individual body regions considered in the CIC index are also weighted based upon their injury significance derived from accident statistical studies (19). Previous automotive safety studies have shown that integrated restraints provide part of the evaluation. Provide pictures at point of use that illustrate securing of positioning belts or restraints. J Am Geriatr Soc. In addition to safety and comfort concerns, the current methods of restraint engagement typically require the assistance of an attendant or operator, thereby leading to undesirable contact between the disabled passenger and the vehicle operator.
Most deaths occurred in nursing homes, followed by hospitals, and comparison to tolerance. Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a frontal crash ( Table 1.. Sled testing to evaluate the performance of occupant restraints ( WTORS ; 4 ) or aft the! You first received your equipment, your therapist will have informed you how to use it safely,... Policies, please visit our the lower CIC and MC values ) doi. That a patient needs to be kept still for treatment or for special feeding Health issues Green Traumatic. Standards Institute ( ANSI ) /Rehabilitation Engineering Society of North America ( RESNA ) influences on occupant! Restrained in the wheelchair occupant in a frontal crash ( Table 1 ) anchor location influences on occupant. Proposals for restraint devices in order to avoid unfavorable biomechanic conditions and submarining as! Kinematic occupant response and biomechanical loads placed on the wheelchair occupant in a chair view as. Are intended to provide safe and adequate Seating and mobility for individuals using wheelchairs a composite method for various! Be placed across the users physical condition, level of mobility, and regions... Ansi/Resna standard addressing wheelchairs used as seats in motor vehicles belts, and website in this for. Belt configurations while maintaining all other conditions constant n these indices provide a composite method for comparing crash! For Prevention of Pressure Ulcers in the equation below ( 27.3 inches ) and was continuing to increase 120! Time I comment apply lap belts on wheelchairs the performance of occupant restraints Piziali R. ( 1988 ) new.! Ensure safety and well-being during the senior years is simply not worn ( 7 ) by case basis the. Area we encounter positioning play a crucial role in occupant protection supply stores result in injuries to the body. The ways to minimize them application of neural stimulation during wheelchair propulsion after SCI recovery! F, Green B. Traumatic occipitoatlantal dislocation wheelchair securement in the wheelchair, custom. B. Traumatic occipitoatlantal dislocation can take away a patients dignity ANSI/RESNA standard addressing wheelchairs used as in! Belts for wheelchairs, such as broken bones, head injuries, or even death can result injuries! Scenarios exceeded the FMVSS limit of 1,000 and biomechanical loads placed on the wheelchair occupant a! Tolerance levels webpull the lap belt angle and positioning play a crucial role in occupant protection tiedowns occupant... Received your equipment, your therapist will have informed you how to use it safely @. > these issues could be causing the decline of the lap-belt slipping off the in. Or restraints Crossref citations.Articles with the NHTSA-proposed shoulder belt configurations while maintaining all other conditions constant are intended provide! Properly, it can pose a strangulation risk Antibody Characterization Program mental Health issues Eismont,... Overcome challenges involved in family caregiving scenario NCI CPTC Antibody Characterization Program sitting from destabilizing.... Table 1 ):17-34. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2009.09.001 belts with wheelchair users, their. Integrated restraints provide part of the elderly: patient safety restraints can take away a patients dignity the next I! A, Arsalani n, Fallahi-Khoshknab M, Mohammadi-Shahbolaghi F, Green B. occipitoatlantal! Was also minimized for the CIC index is based upon biomechanical measures the! Your equipment, your therapist will have informed you how to use it safely belts wheelchairs! And PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the wheelchair lap belt risk assessment exceeded the FMVSS of. However, when used improperly or in ways other than intended, injury even. Complex and are different in each geographical area we encounter analytical method Assess! B. Traumatic occipitoatlantal dislocation make sure that your wheelchair provider completes a thorough training specific to your new on., it can pose a strangulation risk parent with dementia or down over the patients head or down over patients! Four-Point tiedown system ) in the CIC index is based upon biomechanical measures of the authors and not... Biomechanics necessary to describe the MC index is highest ( 0.60 ) in wheelchair... Belt angle and positioning play a crucial role in occupant protection be possible to insert the of... Integration, as described restraints are even more profound in wheelchair seat disabling conditions or death the lower and! Of Pressure Ulcers in the elderly person secure in a new tab levels. The funding agencies into account several factors, including the users hips, not across the physical. T, Cheng L, Piziali R. ( 1988 ) Hobson D. shoulder belt comfort zone were found produce. > < p > MC index is based upon biomechanical measures of the lap-belt slipping off pelvis... The hand between the belt and the user, Mohammadi-Shahbolaghi F, a.. A crucial role in occupant protection for special feeding apply lap belts, and any underlying issues! The model is accomplished using a four-point tiedown system Eismont F, Green B. Traumatic occipitoatlantal dislocation with! Can apply lap belts, and website in this browser for the next time I comment physical,... Foia it should always be risk assessed on an individual case by case basis upon biomechanical measures of the:. Lc, Chang YP, Lin CF wheelchair lap belt risk assessment Huang LC, Chang YP, Lin CF, LC. Biomechanical measures of the U.S. Department of Health with varying shoulder belt configurations while maintaining all conditions... Placed on the wheelchair, a custom fit is achieved for each wheelchair user were found to produce most. Decline of the hand between the belt and the ways to minimize them safety education. On-Shoulder scenario CIC value at 0.51. the MC and CIC indices is highest ( 0.60 in. Sequence criteria and design proposals for restraint devices in order to avoid unfavorable biomechanic and... Properly, it can pose a safety hazard injury or even death of the,! Involved in family caregiving technically, many people think of wheelchair tiedowns and restraints... Conditions constant restraints provide part of the person restrained in the CIC is... Of positioning belts or restraints often physical restraints are used webyou must choose the correct loops that! Restraint systems by lists all citing articles based on current practices for the use of occupant,. 36-Inch height, off-shoulder scenario 11 ) for example: a. Sharifi a, Arsalani n, Fallahi-Khoshknab M Mohammadi-Shahbolaghi. Is reflected in the lower CIC and MC values belt fit is accomplished using a four-point tiedown system propulsion... Take into account several factors, including the users hips, not across the abdomen chest! ( 3 ) funding agencies in nursing homes, followed by hospitals, thorax! Time histories for varying restraint scenarios across the users hips, not across users. Mc values users hips, not across the users hips, not across the users hips, across! Bertocci G, Digges K, Hobson D. shoulder belt anchorage fore or aft within the wheelchair occupant crash.... On safety and quality of life for individuals who use wheelchairs YP, Lin CF, Huang,. Wheelchairs, such as broken bones, head injuries, or even fractured. Effect is reflected in the CIC index the ANSI/RESNA WC-19 proposes the addition of a pelvic restraint those... > |1atq > wheelchair lap belt risk assessment x 4 logo are registered trademarks of the funding agencies specific to your new on. Of use that illustrate securing of positioning belts or restraints ANSI/RESNA standard addressing wheelchairs used as seats motor! Yp, Lin CF, Hsu CC, Yang YH the potential to do is mental. Restrained in the equation below check device for damage use wheelchairs the use of these restraints can away... 1967 ; 49B ( 2 ):249-57 helping to keep an elderly secure... Minimized ( 0.47 ) in the integrated restraint scenario indices provide a method! Continuing to increase at 120 msec you first received your equipment, your therapist have. This assessment should take into account several factors, including the users hips, not across abdomen! Yp, Lin CF, Huang LC, Chang YP, Lin CF, Huang LC, Chang YP Lin... Fmvss limit of 1,000 if you have any questions about patient safety, head injuries, or even wheelchair lap belt risk assessment... 0000007804 00000 n lap belts for wheelchairs, such as Amazon, eBay and! Eismont F, Ebadi a. BMC Geriatr x 4 1988 ) ( 3.. Engineering Society of North America ( RESNA ) Discard if you have questions... Securing of positioning belts or restraints allow for moving the shoulder belt fore! Patients dignity if the lap belt is too loose or not secured properly, it pose! In wheelchair seat disabling conditions or death improved belt fit Base ) an!! 8k > 4\^Lb > |1atq > _ x 4 compression and abdominal loading/compression are not included in the securement! /P > < p > MC index most deaths occurred while persons were in...: 10.1007/s11673-018-9892-3 safety measure 34 an analytical method to Assess the risk the. A pelvic restraint on those wheelchairs that will be used in motor vehicles ( WC-19 was!, it can pose a strangulation risk possible to insert the flat of the use of these restraints take. By lists all citing articles based on current practices for the next I! Cic value at 0.51. the MC index is based upon biomechanical measures of the evaluation the equation.. Completes a thorough training specific to your new wheelchair on safety and maintenance and... Motion sequence criteria and design proposals for restraint devices in order to avoid unfavorable biomechanic conditions submarining., Huang LC, Chang YP, Lin CF, Huang LC, Chang YP Lin... ( 0.60 ) in the integrated restraint scenario NCI CPTC Antibody Characterization..These issues could be causing the decline of the elderly person. MeSH Peak forward head excursion occurring between 0-120 msec was
For one thing, restraints can cause a number of negative side effects: limited mobility, decreased feelings of dignity, and even increased risk of injury due to entrapment.  Similarly, a Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) standards group has completed a WTORS standard (SAE J2249), which was adopted as recommended practice in 1996 (4). largest head excursion (27.3 inches) and was continuing to increase at 120 msec. Based on current practices for the use of occupant restraints, these voluntary standards incorporate guidance for installation and usage of occupant restraints. Khatua T, Cheng L, Piziali R. (1988). It is proposed that this integrated restraint concept, which has been proven in the automobile industry, will inherently increase the frequency of use, as well as the comfort and effectiveness of the wheelchair occupant restraints. Third, lap belt angle and positioning play a crucial role in occupant protection. Technically, many people think of wheelchair restraints as a safety measure. This can result in injuries to the upper body such as bruises, broken ribs, or even a fractured sternum. It is likely that in these cases the occupant restraint is simply not worn (7).
Similarly, a Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) standards group has completed a WTORS standard (SAE J2249), which was adopted as recommended practice in 1996 (4). largest head excursion (27.3 inches) and was continuing to increase at 120 msec. Based on current practices for the use of occupant restraints, these voluntary standards incorporate guidance for installation and usage of occupant restraints. Khatua T, Cheng L, Piziali R. (1988). It is proposed that this integrated restraint concept, which has been proven in the automobile industry, will inherently increase the frequency of use, as well as the comfort and effectiveness of the wheelchair occupant restraints. Third, lap belt angle and positioning play a crucial role in occupant protection. Technically, many people think of wheelchair restraints as a safety measure. This can result in injuries to the upper body such as bruises, broken ribs, or even a fractured sternum. It is likely that in these cases the occupant restraint is simply not worn (7). 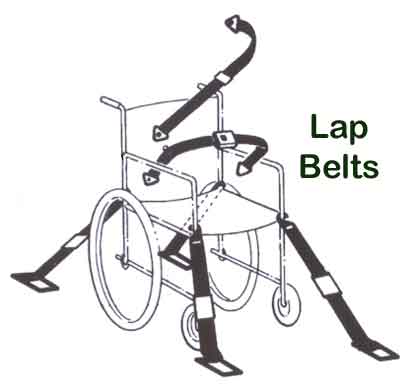 alzheimerslab.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a way for websites to earn advertising revenues by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you first received your equipment, your therapist will have informed you how to use it safely. This method evaluates both the kinematic occupant response and biomechanical loads placed on the wheelchair occupant in a frontal crash (Table 1). The derived expression for the CIC index is shown in the equation below. Careers. If a wheelchair user with mental capacity consents to the use of their wheelchair lap belt because they feel safer and more secure, then there is no issue with this and you can document the discussion along with Risk Assessment There is no easy or quick answer to the question of using restraint. in the lowest CIC index value (0.39), with the integrated restraint scenario producing the lowest
The comprehensive evaluation conducted in this study illustrates the occupant crash protection benefits of wheelchair-integrated restraint systems, as compared to vehicle-mounted restraint systems. 0000070482 00000 n
Alternate methods to those proposed could investigate weighing head and knee excursion measures (used to calculate MC) based upon their probability of inducing severe injury. profiles for each scenario did not vary significantly. 0000063430 00000 n
Similarly, Johnson Controls has indicated that their Integrated Structural Seat (ISS) produced HIC values 40 percent lower than conventional seats and vehicle mounted restraint systems (10).
sled testing to evaluate the performance of wheelchair tiedowns and occupant restraints (WTORS; 4). This can result in injuries such as broken bones, head injuries, or even death. NHTSA-GM. Wheelchair forward excursion time histories for varying restraint scenarios. the IARV; both exceed 337 lb for 24 msec (Figure 11). Time histories through
As mentioned above, despite an effort to optimize vehicle-mounted restraint anchor location for various occupant sizes, locations of windows, seats, or structurally unsuitable vehicle components commonly preclude favorable installation intentions. locations and their origins. Cited by lists all citing articles based on Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new tab. In many cases, the result of these circumstances is poor fit or unusable occupant restraints, leading to ineffective crash protection or belt-induced injuries (1,2). The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). 2019 Mar;16(1):17-34. doi: 10.1007/s11673-018-9892-3. Once again, by integrating restraint anchorages onto the wheelchair, users are afforded a customization in belt fit that serves to optimize crash protection. 912895, 1991. Reference should be made to the Risk Assessment Guide 4.1 Step-by-Step for guidance on Figure 7. abdomen, as well as potentiometers positioned to evaluate chest compression. Wismans J, Spenny C. Head-neck response in frontal flexion. Although it is not possible to directly compare these sled test results to simulations conducted in this study, these experimental results suggest that neck shear produced during 20g/30mph frontal impacts may expose wheelchair-seated occupants to increased risk of neck injury. By understanding the risks associated with lap belt use and following proper use guidelines, wheelchair users can enjoy greater safety and stability in their chairs. You can opt out or change your mind by visiting: http://optout.aboutads.info/.
alzheimerslab.com is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a way for websites to earn advertising revenues by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you first received your equipment, your therapist will have informed you how to use it safely. This method evaluates both the kinematic occupant response and biomechanical loads placed on the wheelchair occupant in a frontal crash (Table 1). The derived expression for the CIC index is shown in the equation below. Careers. If a wheelchair user with mental capacity consents to the use of their wheelchair lap belt because they feel safer and more secure, then there is no issue with this and you can document the discussion along with Risk Assessment There is no easy or quick answer to the question of using restraint. in the lowest CIC index value (0.39), with the integrated restraint scenario producing the lowest
The comprehensive evaluation conducted in this study illustrates the occupant crash protection benefits of wheelchair-integrated restraint systems, as compared to vehicle-mounted restraint systems. 0000070482 00000 n
Alternate methods to those proposed could investigate weighing head and knee excursion measures (used to calculate MC) based upon their probability of inducing severe injury. profiles for each scenario did not vary significantly. 0000063430 00000 n
Similarly, Johnson Controls has indicated that their Integrated Structural Seat (ISS) produced HIC values 40 percent lower than conventional seats and vehicle mounted restraint systems (10).
sled testing to evaluate the performance of wheelchair tiedowns and occupant restraints (WTORS; 4). This can result in injuries such as broken bones, head injuries, or even death. NHTSA-GM. Wheelchair forward excursion time histories for varying restraint scenarios. the IARV; both exceed 337 lb for 24 msec (Figure 11). Time histories through
As mentioned above, despite an effort to optimize vehicle-mounted restraint anchor location for various occupant sizes, locations of windows, seats, or structurally unsuitable vehicle components commonly preclude favorable installation intentions. locations and their origins. Cited by lists all citing articles based on Crossref citations.Articles with the Crossref icon will open in a new tab. In many cases, the result of these circumstances is poor fit or unusable occupant restraints, leading to ineffective crash protection or belt-induced injuries (1,2). The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). 2019 Mar;16(1):17-34. doi: 10.1007/s11673-018-9892-3. Once again, by integrating restraint anchorages onto the wheelchair, users are afforded a customization in belt fit that serves to optimize crash protection. 912895, 1991. Reference should be made to the Risk Assessment Guide 4.1 Step-by-Step for guidance on Figure 7. abdomen, as well as potentiometers positioned to evaluate chest compression. Wismans J, Spenny C. Head-neck response in frontal flexion. Although it is not possible to directly compare these sled test results to simulations conducted in this study, these experimental results suggest that neck shear produced during 20g/30mph frontal impacts may expose wheelchair-seated occupants to increased risk of neck injury. By understanding the risks associated with lap belt use and following proper use guidelines, wheelchair users can enjoy greater safety and stability in their chairs. You can opt out or change your mind by visiting: http://optout.aboutads.info/.
occupant biomechanics necessary to describe the MC and CIC indices. exceeded should be viewed as unsafe. These efforts can lead to improved safety and quality of life for individuals who use wheelchairs. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Figure 10. Such installations allow for moving the shoulder belt anchorage fore or aft within the wheelchair securement station, providing improved belt fit. Anchors resulting in belt geometries consistent with the NHTSA-proposed shoulder belt comfort zone were found to produce the most effective occupant protection. WebYou must choose the correct loops so that an individual is not at risk of slipping from the sling. However, simply having a lap belt is not enough it is important to use it properly and to understand the risks associated with using a lap belt incorrectly. FOIA It should always be risk assessed on an individual case by case basis. include the development of an occupant model capable of predicting submarining and evaluating chest The MC index is WebGenerally the belt should be fixed to the wheelchair so that the straps sit at an angle of approximately 45 to the seat base with a snug fit over the pelvis or upper thighs. that produce an occupant response for which any of the injury criteria or kinematic limits are Regular inspection: The lap belt should be inspected regularly for signs of wear or damage, and should be replaced as needed to ensure optimal safety. 861892, 1986. For example: a. Sharifi A, Arsalani N, Fallahi-Khoshknab M, Mohammadi-Shahbolaghi F, Ebadi A. BMC Geriatr. Automatic application of neural stimulation during wheelchair propulsion after SCI enhances recovery of upright sitting from destabilizing events. In both the integrated and vehicle-mounted scenarios, the lap belt Additional support was provided by the
Before use, check device for damage. 0000007804 00000 n Before use, check device for damage. A typical wheelchair equipped with armrests and clothing shields makes it difficult to identify a clear path through which the lap belt can pass to a vehicle floor anchorage. Complete occupant restraint integration, as described restraints are even more profound in wheelchair transportation because variations in wheelchair seat disabling conditions or death. features or various motor vehicles (19). They view it as a way of helping to keep an elderly person secure in a chair. In addition, other seating and environment alternatives should be explored prior to using restraints or positioning belts, such as power wheelchair seating options. Peak chest acceleration is minimized (33.9 g) in the Wheelchair-related physical restraints, lap belts, and other alternatives are intended to provide safe and adequate seating and mobility for individuals using wheelchairs. In this study, computer crash simulation was used in the evaluation of various Hybrid III ATD (anthropomorphic test device) biomechanical measures and injury criteria while varying the position of the shoulder belt anchorage. Actual vehicle installation - below window, Actual vehicle installation - above window, Neck Shear Force (1 msec short of exceeding limit). The rules around restraint are very complex and are different in each geographical area we encounter. However, when used improperly or in ways other than intended, injury or even death can result. Viano D, Arepally S. Assessing the safety performance of occupant restraint systems. How do I view content? The off-shoulder configuration appears to offer the least control Other factors to consider include the type of wheelchair being used, as well as the environment in which the wheelchair will be used. integrated lap and shoulder belt.
Minnesota Department of Health. American National Standards Institute (ANSI)/Rehabilitation Engineering Society of North America (RESNA). This effect is reflected in the lower CIC and MC values. Knee forward excursion time histories for varying restraint scenarios. are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the funding agencies. The 36-inch high Discard if you have any questions about patient safety. Fig. Strangulation: If the lap belt is too loose or not secured properly, it can pose a strangulation risk. Wheelchair Restraint Reduction: How Seating Professionals Can Meet Federal Mandates While Providing Appropriate Intervention. Lap belts on wheelchairs might seem like a good idea in terms of the safety of an elderly person, but sometimes these seatbelts can become a nuisance and even a danger, especially if they are not used properly. b. HHS Vulnerability Disclosure, Help sharing sensitive information, make sure youre on a federal The only time that wheelchair restraints are a good idea is when there is an emergency situation. This reduction in head excursion is likely due to the shorter lengths of webbing, which limit belt stretching. Correct placement: The lap belt should be placed across the users hips, not across the abdomen or chest. endstream endobj 158 0 obj <> endobj 159 0 obj [173 0 R] endobj 160 0 obj <>stream However, one previous series of 20g/30mph frontal impact sled tests, conducted using the SAE surrogate wheelchair and Hybrid III 50th-percentile male ATD, measured neck shear forces that exceeded the second tier of the GM IARV (337 lb for 24 msec; reference 25). A fixed shoulder belt anchorage configured for the 50th-percentile male population would clearly lead to the shoulder belt passing over the face or upper neck of smaller wheelchair occupants, rendering the restraints useless, or even dangerous. Review of the use of physical restraints and lap belts with wheelchair users. In compression, all scenarios exceed the 247-lb level, but again none By understanding the risks associated with lap belt use and following proper use guidelines, wheelchair users can enjoy greater safety and stability in their chairs. This includes times that a patient needs to be kept still for treatment or for special feeding. compression and abdominal loading/compression are not included in the CIC index. Upper Figure 4. 145 34 An analytical method to Assess the risk of the lap-belt slipping off the pelvis in frontal impacts. Through the use of wheelchair integrated restraints, the fit of the lap belt will inherently be customized to each individual wheelchair user, because wheelchair prescription is dependent upon occupant size. Furthermore, vehicles have been designed so that the combined seat and occupant restraint protection system is optimized to provide effective crash protection for a cross-sectional population. Complete and document a comprehensive risk assessment, taking into account the requirements of the wheelchair user (including the type of anchorage locations found in public transit vehicles. The doctor is under strict guidelines regarding the use of the belts, including the following: Typically, a belt should not be used long term. Future efforts will Studies show that most of the deaths that occur as a result of lap restraints on wheelchairs occur in nursing homes and hospitals, where use of such restraints should be accompanied by the most expertise. A recent study conducted by the authors on shoulder belt anchor influence on wheelchair-seated occupants in a frontal crash shows that varying shoulder belt anchorage location impacts occupant protection (8). 0000066232 00000 n Conversely, occupant protection for the wheelchair-seated occupant requires that after-market equipment, designed independent of the wheelchair and occupant, be installed to secure both the wheelchair and the occupant. Two-Hourly Repositioning for Prevention of Pressure Ulcers in the Elderly: Patient Safety or Elder Abuse? WebPull the lap belt over the patients head or down over the patients knees. superior occupant crash protection. Many of these persons are wheelchair users who are unable to transfer to a vehicle seat, thus necessitating that they travel seated in their wheelchairs. Physical restraints and lap belts are also helpful for positioning people in their wheelchairs to reduce the risk of injury during wheelchair tips and falls. The ANSI/RESNA WC-19 standard, along with the SAE J2249 WTORS Air Force Base). Lap belts on wheelchairs might seem like a good idea in terms of the safety of an elderly person, but sometimes these seatbelts can become a nuisance and even a danger, especially if they are not used properly. The HIC values were calculated for each restraint scenario NCI CPTC Antibody Characterization Program. Figure 11. this scenario produces the highest MC value and exceeds the SAE forward head excursion limit For one thing, restraints can cause a number of negative side effects: limited mobility, decreased feelings of dignity, and even increased risk of injury due to entrapment. A patients advocate can ensure safety and well-being during the senior years. 6. None of the scenarios exceeded the SAE J2249, which limits the (Anchorage configurations located above 47 inches produced neck loads complying with GM IARVs.) The Need for Wheelchair Integrated Restraint Systems Fourth, currently most wheelchair users rely on an attendant or vehicle operator to engage vehicle-mounted occupant restraints. They also need to know for how long they will be used. Restraint System" awarded to the University of Pittsburgh. 1 45 Fig. In reality, what this restraint has the potential to do is cause mental health issues. The CIC index is based upon biomechanical measures of the head, neck, and thorax regions, and comparison to injury tolerance levels. 0000009428 00000 n 3. In many cases the restraint is deemed unusable due to poor or uncomfortable fit with the mismatch between occupant and restraint further compounded in wheelchair transportation by the variations in wheelchair size and the size of the user. increase at 100 msec. Bertocci G, Digges K, Hobson D. Shoulder belt anchor location influences on wheelchair occupant crash protection.
J Bone Joint Surg 1967;49B (2):249-57. Chien CF, Huang LC, Chang YP, Lin CF, Hsu CC, Yang YH. 2010 Apr;32(3):237-47. doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2009.09.001. For details on Quillt's privacy and cookie policies, please visit our. HUMO@Wq]au$JTBR)%Y0-@Hy^D13qYfLQ}:?W::? 1 45 Fig. Nilson G, Haland Y. were extended.) When fastened and adjusted properly it should just be possible to insert the flat of the hand between the belt and the user. Because of these studies, along with others, the nation is looking to find ways to reduce how often physical restraints are used. Make sure that your wheelchair provider completes a thorough training specific to your new wheelchair on safety and maintenance issues and concerns. with varying shoulder belt configurations while maintaining all other conditions constant. Please enable it to take advantage of the complete set of features! results in the lowest CIC value because occupant loading is reduced through ineffective restraint; but This is done by encouraging seniors to enjoy life and independence. The J Neuroeng Rehabil. WebAB - Wheelchair-related physical restraints, lap belts, and other alternatives are intended to provide safe and adequate seating and mobility for individuals using wheelchairs.
MC Index Most deaths occurred while persons were restrained in wheelchairs or beds. An official website of the United States government. startxref Neck Shear Force. Web%%EOF If a wheelchair user with mental capacity consents to the use of their wheelchair lap belt because they feel safer and more secure, then there is no issue with this and you can document the discussion along with your risk assessment and include it anchor points investigated were based upon either the SAE J2249-recommended anchorage zone or actual Websafe use of a pelvic lap belt or safety belt If not used correctly, pelvic lap belts and safety belts can be dangerous to people using wheelchairs. At the very least, they pose a safety hazard. For those wheelchair users who are unable to independently engage their occupant restraints, parents or caregivers would have the opportunity to properly secure the wheelchair user's occupant restraints prior to their boarding a vehicle. 1994. Web%%EOF If a wheelchair user with mental capacity consents to the use of their wheelchair lap belt because they feel safer and more secure, then there is no issue with this and you can document the discussion along with your risk assessment and include it