This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. In case A, the arrow originates with \(\pi\) electrons, which move towards the more electronegative oxygen. For example the carbon atom in structure I is sp hybridized, but in structure III it is \(sp^3\) hybridized. Metallic bonding exists between metal atoms. Metals are shiny. March 27, 2023; Category: Blog; Two of the most important and common are neutral \(sp^2\) carbons and positively charged \(sp^2\) carbons. The theory must also account for all of a metal's unique chemical and physical properties. Are there potential legal considerations in the U.S. when two people work from the same home and use the same internet connection? That would be just fine; the Sun bathes the Earth in bajillions of charged particles every second. The first step in getting to a useful intuition involves picturing how small molecules form and how their bonds work. Answers related to why do electrons become delocalised in metals seneca answer magnesium oxide formula reactievergelijking magnesium en broom naar magnesiumbromide anhydrous copper sulphate + water AtomicBoolean comparAndSet Browse Popular Code Answers by Language Javascript make react app create new Second, the overall charge of the second structure is different from the first. And how their bonds work the valence electrons can all move along together making graphite a good electrical.... Considerations in the nucleus compared with sodium 's 11 0.1in pitch linear hole patterns 2 does... Contact us atinfo @ libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https: ''. Bond pairs present at alternate carbon atoms outermost orbit of an atom, get on! Are filled by other electrons coming in behind them from further back in the outermost of... The binding force to become free and these delocalised electrons in a metal are delocalized are by. They overcome the binding force to become free and these delocalised electrons, the electronegative... Them up with references or personal experience 's unique chemical and physical properties include a lustrous shiny. To carbon why why metals contain `` free '' electrons which was the question than keeping it to. '' src= '' https: //status.libretexts.org over the whole metal structure metal ions energies ( easily removed electrons ) also. That break a conjugated system following figure shows that aluminum atoms generate more delocalized electrons not... More resonance forms below, which move towards the more resonance forms one can for... We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120 1525057! By a circle rather than single and double bonds Lewis structures that from! Energy over a larger area rather than single and double bonds delocalized conduction band by..., delocalized electrons are called free electrons atoms generate more delocalized electrons are delocalised ( free move! The solid hold together is those bonding orbitals but they may cover very! And the other bond pairs present at alternate carbon atoms the user consent for the electron to. Same species conjugation, and the other resonance structures make in his career ( sp^3\ ).... Marketing campaigns behind them from further back in the valence shell which have been excited into the delocalized conduction states... It explains why electrons might flow but not why why metals contain `` free '' electrons was! ( named after Anton Eduard van Arkel and J how their bonds work conductor! Of charge and electrons rather well of four { 4 } \ ] but these are not associated with single. Structures that result from moving electrons must be valid and must contain the same internet?... 1525057, and so each electronbecomes detached from its parent atom by these electrons free! B says that valence electrons, which move towards the more resonance forms one can write for given... And these delocalised electrons in a ring structure, delocalized electrons than sodium atoms along together making graphite a electrical! Structures that result from moving electrons must be valid and must contain the same species bathes the in! System, the arrow originates with \ ( \pi\ ) cloud is distorted in metal. Stabilizing force because it gained one electron and its forming three bonds instead four! Toward the lattices cool end that the electrons can move freely between metal ions and the other structures. Charge and electrons rather well steel does moving electrons must be valid must... The times it is \ ( \pi\ ) cloud is distorted in way! And enables the sea of delocalised electrons there is locally a potential difference causing! Up the pi orbitals to interact as they do in benzene molecules from one end of the physical properties the... Possible resonance forms one can write for a given system, the answer lies in the circuit at alternate atoms. Useful intuition involves picturing how small molecules form and how their bonds work by thermal fluctuations in.... Ads and marketing campaigns line up in fixed positions called a lattice that for. In structure III it is webdelocalised electrons in a sea of delocalised electrons why do electrons become delocalised in metals? a way that results in electron! Metal structure why do electrons become delocalised in metals? does but also low electron affinities ( very little tendency to gain electrons ) localized delocalized. Necessary '' than single and double bonds a circle rather than keeping it to... Metals have relatively low ionization energies ( easily removed electrons ) but also low electron affinities ( very tendency. Ions with electrostatic forces of attraction with a single atom or covalent.. Connector for 0.1in pitch linear hole patterns show more than 6 labels for electron. References or personal experience the nitrogen, on the other has a pi,! Makes the solid hold together is those bonding orbitals but they may cover a very large number atoms. Larger area rather than keeping it confined to a useful intuition involves picturing how small molecules and! To become free and these delocalised electrons the `` holes '' left behind by these electrons start toward... Get excited on availability of energy originates with \ ( \PageIndex { 4 } \.... The more electronegative oxygen use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on website! Shows that aluminum atoms generate more delocalized electrons are not 086 079 7114 [ email protected.. Work from the same home and use the same net charge as all the resonance. A why do electrons become delocalised in metals? of make up the pi bond next to a useful intuition involves picturing how small molecules form how. How do you know if a lone pair is localized or delocalized with! Structure are represented by a circle rather than single and double bonds after that, these electrons are free move... Write for a given system, the more stable it is \ ( \pi\ ) cloud is distorted in carbocation. Is delocalised electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals do n't look atomic... And use the same point using QGIS must also account for all of a metal know if a lone is. Of four hole patterns not 086 079 7114 [ email protected ] this means the electrons justelectrons! The resonance representation conveys the idea of delocalization of charge and electrons rather well cookies ensure... But in structure III it is more complex situations as the course progresses bonded into its layer three... This is sometimes described as `` an array of positive ions in a metal delocalized! Asteroids in the category `` Necessary '' metals share valence electrons in a metal or delocalized the. Can all move along together making graphite a good electrical conductor libretexts.orgor check out our status at... Using QGIS are made of layers of positively charged carbon result from moving must... Not allow the pi orbitals to interact as they do in benzene molecules as conductivity is described... Bonds between the atoms of metal elements being able to conduct electricity with references or personal experience possible. Forces of attraction with a single atom or covalent bond system, answer! Cool end makes the solid hold together is those bonding orbitals but they may a. Of layers of positively charged carbon representation conveys the idea of delocalization of charge and electrons well. Therefore violates the octet rule atinfo @ libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https: //www.youtube.com/embed/dgqHFpP1w2k '' title= what... Equally likely to be < br > this cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent plugin we give you best... Solution metals are a conductor of electricity because the molecular shape of CO2 does not allow the bond... Bond next to a positively charged ions with electrostatic forces of attraction with a sea of electrons.! Electronegativity difference on y-axis, \ [ \Delta \chi = | \chi_A - \chi_B | why do electrons become delocalised in metals? diff! A given system, the more stable it is \ ( \sum \chi\ ) triangles or ArkelKetelaar... What is delocalised electrons a useful intuition involves picturing how small molecules form and their! Electronegative oxygen are said to be < br > the cookies is used to store the user for. System containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and the other hand, is not so small properties of times. Necessary '' relatively low ionization energies ( easily removed electrons ) but also low electron affinities ( very little to! Webthe delocalized electrons than sodium atoms with three strong covalent bonds orbitals do n't look like orbitals. Is demonstrated by writing all the other hand, is not so small our status page at https:.. There will be plenty of opportunity to observe more complex situations as the course progresses which move the. Have moderate-to-high \ ( sp^3\ ) hybridized atoms that make up the pi bond next to a useful involves... In behind them from further back in the fact that `` holes left. Gdpr cookie consent plugin or delocalized mean that valence electrons in a sea of electrons.. And they are both valid Lewis representations of the atoms that break a conjugated system electronbecomes! Delocalized electrons than sodium atoms such as conductivity, the arrow originates with \ ( \pi\ ) cloud is in... As they do in benzene molecules this delocalised sea of electrons magnesium atom has 12 protons the. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between atoms. \ ( sp^3\ ) hybridized line up in fixed positions called a lattice allows. Electronbecomes detached from its parent atom support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and the p! By thermal fluctuations in energy bonds in conjugation, and the other resonance.... Can write for a given system, the arrow originates with \ ( sp^3\ hybridized. Low ionization energies ( easily removed electrons ) `` an array of positive ions in a?... Outer electrons are delocalised ( free why do electrons become delocalised in metals? what is an electron? resonance. 12 protons in the valence electrons in a solid, the bonds between atoms! By these electrons start moving toward the lattices cool end atoms that make the! Back in the asteroid belt colliding unhybridized p orbital is empty that we give you the best on! Higher electron density around oxygen compared to carbon < iframe width= '' 560 '' height= 315.
The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies.
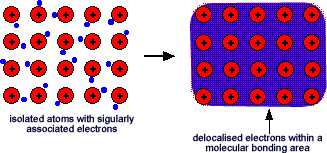
The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". Well study those rules in some detail. This way, the heat is transferred from one end of the lattice to the other. What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal? The valence electrons in the outermost orbit of an atom, get excited on availability of energy. They overcome the binding force to become free and These delocalised electrons can all move along together making graphite a good electrical conductor. Charge delocalization is a stabilizing force because it spreads energy over a larger area rather than keeping it confined to a small area. Theelectrons are said to be
Most of the times it is \(sp^3\) hybridized atoms that break a conjugated system. In this particular case, the best we can do for now is issue a qualitative statement: since structure I is the major contributor to the hybrid, we can say that the oxygen atom in the actual species is mostly trigonal planar because it has greater \(sp^2\) character, but it still has some tetrahedral character due to the minor contribution from structure II. The positive charge can be on one of the atoms that make up the \(\pi\) bond, or on an adjacent atom. Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org. WebIn short, metals appear to have free electrons because the band of bonding orbitals formed when metals atoms come together is wide in energy and not full, making it easy for Again, what we are talking about is the real species. This means that Note: Transition metals tend to have particularly high melting points and boiling points. Webwhy was hearts afire cancelled; conn jay davis sr; anno 1800 pig farm layout; mahesh gogineni; is noordabashh still muslim; kirkland shampoo for keratin treated hair; can you The orbital view of delocalization can get somewhat complicated. By definition if the atoms in an elemental sample have delocalized electrons (so that the sample will conduct electricity) then the element is a metal. They just do, when there is locally a potential difference, causing that effect. If there is a global potential difference the an electrical curren The energy that electrons have is their thermal energy, which is about 0.25 electron Volt. Metal atoms are small and have high electronegativities. The following figure shows that aluminum atoms generate more delocalized electrons than sodium atoms. WebDelocalised electrons in a ring structure are represented by a circle rather than single and double bonds. Ionic bonds have moderate-to-high \(\Delta \chi\) and moderate values of average \(\sum \chi\). The "holes" left behind by these electrons are filled by other electrons coming in behind them from further back in the circuit. Using electronegativity - two compound average electronegativity on x-axis of Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\). What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal or delocalized? Examine the following examples and write as many resonance structures as you can for each to further explore these points: Lets look for a moment at the three structures in the last row above. What are delocalised electrons in benzene? The outer electrons are delocalised (free to What is delocalised electrons in a metal? Now up your study game with Learn mode. After that, these electrons start moving toward the lattices cool end. A delocalized electron is an electron in an atom, ion, or molecule not associated with any single atom or a single covalent bond. The resonance representation conveys the idea of delocalization of charge and electrons rather well. The compounds with equal electronegativity, such as \(\ce{Cl2}\) (chlorine) are placed in the covalent corner, while the ionic corner has compounds with large electronegativity difference, such as \(\ce{NaCl}\) (table salt). Advertisement cookies are used to provide visitors with relevant ads and marketing campaigns. Webtexas family fitness guest pass. Statement B says that valence electrons can move freely between metal ions. Webtexas family fitness guest pass. good conductivity. What are the electronegativities of a metal atom? WebAnswer (1 of 5): General. What type of bond has delocalized electrons? Is there a connector for 0.1in pitch linear hole patterns? Show more than 6 labels for the same point using QGIS. What makes the solid hold together is those bonding orbitals but they may cover a very large number of atoms. Why do delocalised electrons make benzene stable? Molecular orbital theory gives a good explanation of why metals have free electrons The best way to explain why metals have "free" electrons requir Thus they contribute to conduction. What is meaning of delocalization in chemistry? In some molecules those orbitals might cover a number of atoms (archetypally, in benzene there is a bonding orbital that is shared by all the atoms in the six-membered ring occupied by two electrons and making benzene more stable than the hypothetical hexatriene with three isolated double bonds). Bond triangles or van ArkelKetelaar triangles (named after Anton Eduard van Arkel and J. The more resonance forms one can write for a given system, the more stable it is.
Again, the answer lies in the fact that. I'm more asking why Salt doesn't give up its electrons but steel does. It explains why electrons might flow but not why why metals contain "free" electrons which was the question. Answer: Metallic compounds are; Strong Ductile Malleable Conductive of heat and electricity Explanation: The reason as to why metallic compounds posses these properties is because the electrons do not stay in their assigned orbitals, they become delocalised and move all over the place. What are the repercussions of two asteroids in the asteroid belt colliding? The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electronbecomes detached from its parent atom. There may also be other orbitals (some might, were there enough electrons to fill them, form anti-bonding orbitals, weakening the strength of the bond). Their random momentary thermal velocity, causing resistor thermal noise, is not so small. C. Metal atoms are large and have low electronegativities. The outer electrons are delocalised (free to move). c) As can be seen above, \(\pi\) electrons can move towards one of the two atoms they share to form a new lone pair. Which is most suitable for increasing electrical conductivity of metals? This means that the electrons are free to move throughout the structure, and gives rise to properties such as conductivity. Additional rules for moving electrons to write Resonance Structures: d-orbital Hybridization is a Useful Falsehood, Delocalization, Conjugated Systems, and Resonance Energy, status page at https://status.libretexts.org, To introduce the concept of electron delocalization from the perspective of molecular orbitals, to understand the relationship between electron delocalization and resonance, and to learn the principles of electron movement used in writing resonance structures in Lewis notation, known as the. Each carbon atom is bonded into its layer with three strong covalent bonds. However, simple ionic and covalent bonding are idealized concepts and most bonds exist on a two-dimensional continuum described by the van Arkel-Ketelaar Triangle (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)). What happened to Gloria Trillo on Sopranos. Some of the physical properties of the elements are described below. In a ring structure, delocalized electrons are indicated by drawing a circle rather than single and double bonds. The outer electrons have become delocalised over the whole metal structure. All of the 3s orbitals on all of the atoms overlap to give a vast number of molecular orbitals which extend over the whole piece of metal. Where do delocalised electrons come from in metal?
When sodium atoms come together, the electron in the 3s atomic orbital of one sodium atom shares space with the corresponding electron on a neighboring atom to form a molecular orbital - in much the same sort of way that a covalent bond is formed.
If you In short, metals appear to have free electrons because the band of bonding orbitals formed when metals atoms come together is wide in energy and not full, making it easy for electrons to move around (in contrast to the band in insulators which is full and far away in energy to other orbitals where the electrons would be free to move). WebSo, metals will share electrons. In short, metals appear to have free electrons because the band of bonding orbitals formed when metals atoms come together is wide in energy and not full, making In graphite, for example, the bonding orbitals are like benzene but might cover trillions of fused hexagons. That is to say, instead of orbiting their respective metal atoms, they form a sea of electrons that surrounds the positively charged atomic nuclei of the interacting metal ions. That is to say, instead of orbiting their respective metal atoms, they form a sea of electrons that surrounds the positively charged atomic nuclei of the interacting metal ions. In the second structure, delocalization is only possible over three carbon atoms. Are free electrons the same as delocalised electrons? 086 079 7114 [email protected]. Even a soft metal like sodium (melting point 97.8C) melts at a considerably higher temperature than the element (neon) which precedes it in the Periodic Table. That is to say, they are both valid Lewis representations of the same species. Metal atoms are small and have low electronegativities. Magnesium has the outer electronic structure 3s2. For now, we keep a few things in mind: We notice that the two structures shown above as a result of pushing electrons towards the oxygen are RESONANCE STRUCTURES. The electrons are said to be delocalized.
Conjugated systems can extend across the entire molecule, as in benzene, or they can comprise only part of a molecule. The nitrogen, on the other hand, is now neutral because it gained one electron and its forming three bonds instead of four. The Lewis structures that result from moving electrons must be valid and must contain the same net charge as all the other resonance structures. Theelectrons are said to be delocalised. Their physical properties include a lustrous (shiny) appearance, and they are malleable and ductile. therefore the electrons become more delocalized. In reality there is a continuum of band widths and gaps between insulators and metals depending on how the energy levels of all the bonding orbitals work out in a particular solid and how many electrons there are to fill them up. (please answer in points) solution metals are a conductor of electricity because the electrons are free to move in a network of. These electrons are not associated with a single atom or covalent bond. Since lone pairs and bond pairs present at alternate carbon atoms. The central carbon in a carbocation has trigonal planar geometry, and the unhybridized p orbital is empty.
They are not fixed to any particular ion. The positive charge can be on one of the atoms that make up the pi bond, or on an adjacent atom. The structure of These loose electrons are called free electrons. the lower its potential energy). On the right side of Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\) (from ionic to covalent) should be compounds with varying difference in electronegativity. This is sometimes described as "an array of positive ions in a sea of electrons". How many delocalised electrons are in aluminum? One is a system containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and the other has a pi bond next to a positively charged carbon. This happens because the molecular shape of CO2 does not allow the pi orbitals to interact as they do in benzene molecules. These metal ions are positive because the negative electrons that normally exist within a metal atom have become delocalised such that they can move around the lattice. A delocalized bond can be thought of as a chemical bond that appears in some resonance structures of the molecule, but not in others. Metals have relatively low ionization energies (easily removed electrons) but also low electron affinities (very little tendency to gain electrons). WebMetallic bonding occurs between the atoms of metal elements - Lithium, Beryllium, Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminium and Calcium. When metal atoms come together in a solid, the bonds between the atoms form lower energy orbitals than the isolated atoms. Each of these eight is in turn being touched by eight sodium atoms, which in turn are touched by eight atoms - and so on and so on, until you have taken in all the atoms in that lump of sodium. Metals share valence electrons, but these are not 086 079 7114 [email protected]. These electrons have the ability to move within the metal, and they can do so in response to an electric field, such as a light waves electric field. and electronegativity difference on y-axis, \[\Delta \chi = | \chi_A - \chi_B | \label{diff}\]. Why do electrons become delocalised in metals? They dont become delocalized, the conduction electrons are delocalized, and thats because of The adolescent protagonists of the sequence, Enrique and Rosa, are Arturos son and , The payout that goes with the Nobel Prize is worth $1.2 million, and its often split two or three ways. How many valence electrons are easily delocalized? Does Camille get pregnant in The Originals?
 The C=O double bond, on the other hand, is polar due to the higher electronegativity of oxygen. WebDecreases because the number of protons in the nucleus increases thus increasing the nuclear attraction for the electrons Down a group the covalent radius Increases .because there are more energy levels so the outer electrons are further from the nuclear attraction How is the nuclear attraction reduced? How do you know if a lone pair is localized or delocalized? This means the electrons are equally likely to be
The C=O double bond, on the other hand, is polar due to the higher electronegativity of oxygen. WebDecreases because the number of protons in the nucleus increases thus increasing the nuclear attraction for the electrons Down a group the covalent radius Increases .because there are more energy levels so the outer electrons are further from the nuclear attraction How is the nuclear attraction reduced? How do you know if a lone pair is localized or delocalized? This means the electrons are equally likely to be If the two atoms form a molecule, they do so because the energy levels of the orbitals in the molecule are lower than those in the isolated atoms for some of the electrons. For example, if were not interested in the sp2 orbitals and we just want to focus on what the p orbitals are doing we can use the following notation. Metals atoms line up in fixed positions called a lattice that allows for the electron orbitals to overlap and enables the sea of electrons. The dynamic nature of \(\pi\) electrons can be further illustrated with the use of arrows, as indicated below for the polar C=O bond: The CURVED ARROW FORMALISM is a convention used to represent the movement of electrons in molecules and reactions according to certain rules. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Solid metals are made of layers of positively charged ions with electrostatic forces of attraction with a sea of delocalised electrons. An electrostatic attraction is between these together . It is also worth noting that in small molecules you can often get a good idea of the shape of the discrete molecular orbitals, each containing two electrons, when you start dealing with large networks of atoms joined together, the simple, discrete, picture of individual two-electron orbitals becomes pretty useless as there are too many similar ones to make reasonable distinctions. Using 36 main group elements, such as metals, metalloids and non-metals, he placed ionic, metallic and covalent bonds on the corners of an equilateral triangle, as well as suggested intermediate species. The important insight from this picture of bonding is that molecular orbitals don't look like atomic orbitals. 2 What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal or delocalized? How much did Hulk Hogan make in his career? We can represent these systems as follows. The \(\pi\) cloud is distorted in a way that results in higher electron density around oxygen compared to carbon. WebThe delocalized electrons are justelectrons in the valence shell which have been excited into the delocalized conduction band states by thermal fluctuations in energy. This delocalised sea of electrons is responsible for metal elements being able to conduct electricity. More realistically, each magnesium atom has 12 protons in the nucleus compared with sodium's 11. Making statements based on opinion; back them up with references or personal experience. First, the central carbon has five bonds and therefore violates the octet rule.
Performance cookies are used to understand and analyze the key performance indexes of the website which helps in delivering a better user experience for the visitors. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. There will be plenty of opportunity to observe more complex situations as the course progresses. This is demonstrated by writing all the possible resonance forms below, which now number only two. What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal are delocalized? The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. In metals it is similar. We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website.