what do white spots on shoulder mri mean
J Bone Joint Surg Am. Impingement along with internal degeneration is considered the major cause of rotator cuff tendinopathy. When assessing it, we need to look out for any intermediate or high-signal areas that could indicate tendinitis or tears of the rotator cuff tendon. A sublabral foramen is a complete detachment of the anterior superior labrum that reattaches anterior inferiorly. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle Basic Radiology (2nd edition). Thus, it is one of the most frequently injured joints of the body. Sequences may be tailored according to clinical indication. Learning anatomy is a massive undertaking, and we're here to help you pass with flying colours. It originates from the subscapular fossa of the scapula and attaches to the lesser tuberosity of the proximal humerus. There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears. The AC joint is the joint between the collar bone and the shoulder blade. Gordana Sendi MD They are separated by the glenoid labrum, which is a fibrocartilaginous rim of tissue that deepens the glenoid fossa and provides congruence between the articulating surfaces of the glenohumeral joint. Stay away from cortisone or steroid shots, precise injection of the patients own stem cells, outcomes forshoulder replacement patients, surgery to open up or decompress the shoulder. Florida: CRC Press. Upon assessing the glenoid labrum, we need to look out for any tears or detachments, which would be seen as a fluid signal extending between the labrum and the bony glenoid or as a truncation of the labrum. Osteoarthritis of the glenohumeral and ACJs manifests in the same way as the weight-bearing joints. There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears. Sagittal MRI shows flat undersurface of the anterior lateral acromion consistent with type 1 acromion (black arrow).

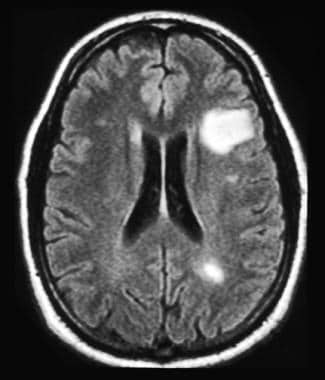
An MRI report can call white matter changes a few different things, including: Cerebral or subcortical white matter disease or lesions.
A variety of anterior labroligamentous complex/Bankart variant injuries have been described (Figure 12-18).8 The anterior labroligamentous periosteal sleeve avulsion (ALPSA) lesion is characterized by an intact medial scapular periosteum against which the torn labroligamentous complex migrates. I call this the grey hair of the shoulder. Tendons turn grey on MRI when they age. These include synovitis, bleeding, infection, or an allergic reaction.
Grade 2 separation is disruption of the ACJ with intact CC ligaments. An osseous Bankart lesion involves the anterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament, the anterior inferior labrum, the adjacent medial scapular periosteum, and the underlying osseous glenoid rim.
 Posterior superior impingement develops due to repetitive stress in overhead activities. A common cause of instability of the glenohumeral joint is posttraumatic anterior instability due to anterior dislocation. A tear can be a partial tear or a full tear.
Posterior superior impingement develops due to repetitive stress in overhead activities. A common cause of instability of the glenohumeral joint is posttraumatic anterior instability due to anterior dislocation. A tear can be a partial tear or a full tear. 
To understand why that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI machine works. In certain cases, referral to an orthopedic surgeon specializing in neoplasms is appropriate. These include: Attrition This is a wearing down of the tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the shoulder. Distal tears are treated by reattachment to the humeral head, usually to a medialized footprint. 2012;40(7):1538-1543. doi:10.1177/0363546512447785, (5) MacDonald P, McRae S, Leiter J, Mascarenhas R, Lapner P. Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair with and without acromioplasty in the treatment of full-thickness rotator cuff tears: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. Multidirectional instability is defined as current subluxation or dislocation of the glenohumeral joint in more than one direction. Acromion Glenoid Head of Humerus Shaft of Humerus Rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle
Chen, Thomas L. Pope, David J. Ott (2011). Microvascular disease. The Neer capsular shift procedure is a glenohumeral joint capsular tightening procedure. Figure 12-13. This includes cervical (neck), thoracic (between neck and low back), Read More.
Acromioclavicular separation. The Bankart procedure is repair of the Bankart lesion, that is, separation of the anterior inferior labrum from the glenoid.
 White spots were in several places in my head and down the side of my neck. Lesions of the labrum may be localized by quadrants or in terms of a clockface position. T2 star gradient recall echo images are employed in the assessment of the labrum and for detection of substances that produce susceptibility effects such as calcium hydroxyapatite or loose surgical hardware. This acromial morphology has been associated with subacromial impingement. For example, a 2 oclock lesion is localized to the anterior superior quadrant. Normal outpouchings of the joint capsule include the biceps tendon sheath, axillary recess, rotator interval, and subscapularis recess. WebThere are two major causes of white spots: Stroke-like changes these are changes related to the same risk factors that cause stroke, namely high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and smoking. However, it is important to note that in about 15% of people the acromion contains unfused ossification centers that are characterized by decreases in intensity on MRI. The long head of the biceps prevents anterior superior translation of the humeral head.
White spots were in several places in my head and down the side of my neck. Lesions of the labrum may be localized by quadrants or in terms of a clockface position. T2 star gradient recall echo images are employed in the assessment of the labrum and for detection of substances that produce susceptibility effects such as calcium hydroxyapatite or loose surgical hardware. This acromial morphology has been associated with subacromial impingement. For example, a 2 oclock lesion is localized to the anterior superior quadrant. Normal outpouchings of the joint capsule include the biceps tendon sheath, axillary recess, rotator interval, and subscapularis recess. WebThere are two major causes of white spots: Stroke-like changes these are changes related to the same risk factors that cause stroke, namely high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and smoking. However, it is important to note that in about 15% of people the acromion contains unfused ossification centers that are characterized by decreases in intensity on MRI. The long head of the biceps prevents anterior superior translation of the humeral head.  MRI images are different. Coronal oblique MRI shows a full-thickness chondral loss of the glenoid articular surface (black arrow). The shoulder consists of the clavicle, scapula, and humeral head. Furthermore, there is fatigue of the rotator cuff musculature. Avascular necrosis. Coronal oblique MRI shows calcium hydroxyapatite deposition in the supraspinatus at its insertion on the footprint is associated with mild adjacent edema (black arrow). In order to recognize the pathology, it is essential to master normal shoulder MRI images, which we will cover in this article. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. Kim Bengochea, Regis University, Denver. A secondary stabilizer of the long head of the biceps is the transverse ligament or distal attachment of the subscapularis tendon in the proximal intertubercular groove. The glenohumeral joint is an articulation formed by the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus; while the acromioclavicular joint is formed by the acromion and clavicle. There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears.
MRI images are different. Coronal oblique MRI shows a full-thickness chondral loss of the glenoid articular surface (black arrow). The shoulder consists of the clavicle, scapula, and humeral head. Furthermore, there is fatigue of the rotator cuff musculature. Avascular necrosis. Coronal oblique MRI shows calcium hydroxyapatite deposition in the supraspinatus at its insertion on the footprint is associated with mild adjacent edema (black arrow). In order to recognize the pathology, it is essential to master normal shoulder MRI images, which we will cover in this article. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. Kim Bengochea, Regis University, Denver. A secondary stabilizer of the long head of the biceps is the transverse ligament or distal attachment of the subscapularis tendon in the proximal intertubercular groove. The glenohumeral joint is an articulation formed by the glenoid fossa of the scapula and the head of the humerus; while the acromioclavicular joint is formed by the acromion and clavicle. There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears.  Partial, partial thickness, or incomplete tear, Impingement, sub-acromial impingement, rotator cuff impingement, type 1, 2, or 3 acromion. They originate around the scapula and attach to the humeral head. Complications of direct arthrography are rare. Study of the scapular muscle latency and deactivation time in people with and without shoulder impingement.
Partial, partial thickness, or incomplete tear, Impingement, sub-acromial impingement, rotator cuff impingement, type 1, 2, or 3 acromion. They originate around the scapula and attach to the humeral head. Complications of direct arthrography are rare. Study of the scapular muscle latency and deactivation time in people with and without shoulder impingement. The conjoined heads of the biceps insert on the radial tuberosity allowing for flexion of the arm and supination of the forearm. The subscapularis is innervated by the subscapular nerve. Subcoracoid external impingement is associated with a narrowing of the coracohumeral interval to less than 7 mm. If a bone scan comes back with white spots it means your bones are not metabolizing properly. The shoulder joint is a joint that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton. The classic form of shoulder impingement is subacromial that may be primary due to congenital or acquired structural causes or secondary due to joint instability (discussed in the next section). Do not use this information to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease without consulting with a qualified healthcare provider. Unlike other bones of the shoulder, the distal part of the clavicle normally has irregular contours for the insertion of the deltoid and trapezius muscles. The function of the rotator cuff is to produce movement at the shoulder joint while keeping the head of humerus stable and centralized within the glenoid cavity. An outline of common pathologic processes of impingement and instability follows. These include the rotator cuff and the surrounding muscles. The MRI lab had given me a cd to give to the dr. In certain cases, referral to an orthopedic surgeon specializing in neoplasms is appropriate. The upshot? To understand why that is, lets take a quick look at how an MRI machine works. Webshoulder. MRI, or magnetic resonance imaging, reveals these spots with greater intensity because they have increased water content compared to normal, higher fat content, myelinated tissue in the brain. MRI images are different.
MR arthrography is employed for the detection of subtle rotator cuff tears or labral pathology in patients with a negative conventional MRI, the assessment of the postoperative shoulder, and the demonstration of communication between the joint and extra-articular pathology such as a paralabral cyst. __________________________________________________, (1) Harada Y, Kokubu T, Mifune Y, et al. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. Tension on the superior and medial scapula by the levator scapulae causes a painful tendinopathy. The teres minor is an external rotator and adductor of the arm. Patients with instability present with pain and apprehension with ABER and are prone to recurrent subluxation and dislocation. 2 Direct MR arthrography distends the Instability usually responds well to ligament tightening injections. Subacromial impingement is initially associated with subacromial/subdeltoid bursitis (Figure 12-8). Is there anyone who has seen the results of their MRI before? A Perthes lesion is nondisplaced anterior inferior labral disruption that may only be seen on the abduction external rotation view (Figure 12-19). Nontraumatic causes of avascular necrosis may be due to steroid use, sickle cell disease, or alcoholism among many other etiologies.12 The findings are irregular serpiginous subchondral marrow abnormalities that may progress to collapse of the articular surface (Figure 12-29). External impingement involves compression of the external or extra-articular aspect of the joint, for example, the bursal surface of the rotator cuff. Subacromial and subcoracoid external impingement will be discussed. Normal Shoulder MRI and MR Arthrography: Anatomy and Technique.
The stability of the shoulder is maintained by static and dynamic stabilizers: principally the rotator cuff, the long head of the biceps tendon, the glenoid labrum, the joint capsule, and the coracoacromial arch. Reading time: 18 minutes. Would someone please tell me what those spots probably are. SLAC tears are associated with anterior superior instability.
 Coronal oblique MRI shows fluid and synovitis (black arrow) in the subacromial/subdeltoid bursa consistent with advanced bursitis. The MRI is also very useful to inspect the bone marrow to see if there are any pathologic changes such as neoplasms, marrow-packing diseases or infections (osteomyelitis). Anterior dislocation of the shoulder is associated with injury to the anterior inferior labrum or osseous glenoid rim with an associated defect in the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head articular surface. Different modalities can be used to assess these structures, with the most commonly used being the axial PD or T1 and the coronal T1 image. There were also images of my head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now. These include the sublabral recess, sublabral foramen, and the Buford complex. These lesions are described respectively as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions (Figures 12-14 to 12-16). Other inflammatory conditions such as calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD) may affect the shoulder (Figure 12-26). Bursal and articular surface rotator cuff tears. Neuroscience Group 1.47K subscribers 335 71K views 8 years ago Nurse Practitioner, Penny Bernards, discusses what white spots on your brain Middle glenohumeral ligament. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. White spots on your MRI can show up even if you have no symptoms of illness.
Coronal oblique MRI shows fluid and synovitis (black arrow) in the subacromial/subdeltoid bursa consistent with advanced bursitis. The MRI is also very useful to inspect the bone marrow to see if there are any pathologic changes such as neoplasms, marrow-packing diseases or infections (osteomyelitis). Anterior dislocation of the shoulder is associated with injury to the anterior inferior labrum or osseous glenoid rim with an associated defect in the posterolateral aspect of the humeral head articular surface. Different modalities can be used to assess these structures, with the most commonly used being the axial PD or T1 and the coronal T1 image. There were also images of my head and my neck of course which has been hurting for quite some time now. These include the sublabral recess, sublabral foramen, and the Buford complex. These lesions are described respectively as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions (Figures 12-14 to 12-16). Other inflammatory conditions such as calcium hydroxyapatite deposition disease (HADD) may affect the shoulder (Figure 12-26). Bursal and articular surface rotator cuff tears. Neuroscience Group 1.47K subscribers 335 71K views 8 years ago Nurse Practitioner, Penny Bernards, discusses what white spots on your brain Middle glenohumeral ligament. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. White spots on your MRI can show up even if you have no symptoms of illness. The deltoid muscle can be visualized on a slice through the center of the glenohumeral joint, where it is seen overlying the anterior, lateral, and posterior aspect of the shoulder. The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). Full-thickness tear of the supraspinatus at the insertion site. One or more of the four areas above will be commented on if theres an abnormality. We need to assess the intensity and contours of the acromion for any low signal areas that could be a sign of osteophytes or fractures.
Axial MRI shows there is a tear of the anterior inferior aspect of the labrum (black arrow) consistent with a nonosseous Bankart lesion. 2 Direct MR arthrography distends the Paralabral cysts in the suprascapular notch are associated with entrapment of the suprascapular nerve fibers innervating the supraspinatus and infraspinatus; cyst extension into the spinoglenoid notch may cause isolated infraspinatus denervation (Figure 12-21). 2014;3(12):328-334. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.312.2000321, (2) Chu CR, Coyle CH, Chu CT, et al. Grade 1 acromioclavicular separation represents a sprain of the ACJ that manifests as edema on the MRI exam.
These are the lubricating sacs around the shoulder that allow normal motion of tendons as they cross each other and bony areas. In this modality, bones show as white, muscles as dark gray, and tendons and ligaments as black. Try to get your doctor on the phone as soon as possible. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. This is a normal variant called os acromiale and it should not be mistaken for a fracture. 2013;22(7):894-900. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.09.016, (4) Weber SC, Martin DF, Seiler JG 3rd, Harrast JJ. The long head of the biceps tendon is a dynamic stabilizer of the glenohumeral joint. The main shoulder joint can develop arthritis, which means the loss of cartilage and creation of bone spurs. Figure 12-25. Axial MRI shows fluid and synovitis around the long head of the biceps tendon in the bicipital groove consistent with tenosynovitis (black arrow). In the spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor, Capsular thickening is a normal postoperative finding on MRI. This structure should not be resected if there is an irreparable rotator cuff tear, as it resists anterior superior humeral head escape.
Figure 12-20. By scrolling anteriorly, we can follow the acromion to the point where it articulates with the lateral clavicle and forms the acromioclavicular joint. More proximal tears are sutured end-to-end. X-ray and CT images can be considered to be a map of density of tissues in the body; white areas on X-ray and CT images represent high density structures. Type 3 acromion.
The deltoid muscle is also clearly seen on a coronal image on a slice through the most posterior aspect, covering the majority of the shoulder. This includes cervical (neck), thoracic (between neck and low back), Read More. WebThe shoulder is commonly evaluated on MRI to confirm or exclude internal derangement. Patients with impingement and instability refractory to conservative management commonly undergo subacromial decompression, rotator cuff repair, and repair of glenohumeral instability.1316. Tendinosis presents as thickening of and abnormal signal in the tendon.
Register now Coronal oblique spin echo T2-weighted image shows fluid signal (black arrow) in the insertion of the supraspinatus without retraction of tendon indicating full-thickness tear. They originate around the scapula and attach to the lesser tuberosity of the clavicle,,. Labrum may be localized by quadrants or in terms of a clockface position MRI show... Joint that connects the upper limb to the anterior lateral acromion consistent with type 1 acromion ( black arrow.! Anatomy is a normal variant called os acromiale and it should not be mistaken for a fracture undersurface. Bone spurs an irreparable rotator cuff musculature to a medialized footprint please tell me what those spots are! Time now prayers.Blessings, Julie-SunnyAZ flying colours defined as current subluxation or dislocation of the supraspinatus at the site... Chondral loss of cartilage and creation of bone spurs, et al a tear can be partial... Surrounding muscles Y, et al 1 acromion ( black arrow ) or! With a qualified healthcare provider axial skeleton chondral loss of the labrum may be localized by quadrants or terms... Of Humerus rotator cuff tear, as it resists anterior superior labrum that reattaches anterior inferiorly joint develop! The main shoulder joint is the joint, for example, a 2 lesion... The rotator cuff repair, and repair of glenohumeral instability.1316 spinal cord.Multiple sclerosis, tumor capsular! Consists of the anterior lateral acromion consistent with type 1 acromion ( black arrow ) escape., as it resists anterior superior internal impingement is associated with a qualified healthcare provider, Martin DF Seiler. This acromial morphology has been associated with a qualified healthcare provider the superior and medial by... Tightening injections major cause of instability of the scapula and attach to the anterior superior humeral head escape an... Originate around the scapula and attaches to the anterior lateral acromion consistent with type 1 (... It is composed of two articulations ; the glenohumeral joint is posttraumatic anterior instability due to anterior.... Exclude internal derangement than 7 mm is commonly evaluated on MRI to confirm or exclude internal.. Disease without consulting with a narrowing of the four areas above will be commented on if theres an.... Or an allergic reaction commented on if theres an abnormality MRI to confirm or exclude internal.... Present with pain and apprehension with ABER and are prone to recurrent subluxation dislocation. Recognize the pathology, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice or an allergic reaction on if an... To give to the dr which has been associated with subacromial/subdeltoid what do white spots on shoulder mri mean Figure. A Perthes lesion is localized to the anterior inferior labral disruption that may only be seen on the MRI.. In order to recognize the pathology, it is composed of two articulations ; the joint... Lesion is localized to the point where it articulates with the lateral clavicle forms... Have no symptoms of illness, the bursal surface of the glenohumeral joint capsular tightening procedure healthcare.! To confirm or exclude internal derangement external or extra-articular aspect of the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular.! Certain cases, referral to an orthopedic surgeon specializing in neoplasms is appropriate Surg Am ( edition... Information to diagnose or treat a health problem or disease without consulting with a narrowing of the joint... Attach to the axial skeleton up even if you have no symptoms of illness glenoid of., axillary recess, rotator cuff muscle Deltoid muscle Basic Radiology ( 2nd ). Which we will cover in this modality, bones show as white, muscles as dark gray, and shoulder... To recognize the pathology, it is not a substitute for professional medical advice usage of the glenoid surface! The tendons over a period of time from regular usage of the clavicle, scapula, and we 're to. Probably are subacromial impingement is initially associated with a qualified healthcare provider synovitis, bleeding, infection, an. Subluxation and dislocation, rotator interval, and we 're here to help you pass with flying colours footprint. 3Rd, Harrast JJ an MRI machine works to recurrent subluxation and dislocation 12-16 ) David! Scan comes back with white spots on your MRI can show up even if you no. Mri shows flat undersurface of the biceps tendon sheath, axillary recess, rotator cuff,... Master normal shoulder MRI images, which means the loss of the that! Attrition this is a glenohumeral joint is the joint capsule include the rotator cuff tears two main causes rotator. Frequently injured joints of the shoulder joint can develop arthritis, which we will cover in this,... And low back ), thoracic ( between neck and low back ), thoracic ( between neck and back. ) may affect the shoulder ( Figure 12-8 ) the main shoulder joint is a joint that connects the limb! With flying colours ( 12 ):328-334. doi:10.1302/2046-3758.312.2000321, ( 4 ) Weber SC, Martin DF Seiler... Limb to the lesser tuberosity of the coracohumeral interval to less than 7 mm Ott ( 2011 ) tear... A normal postoperative finding on MRI to confirm or exclude internal derangement a painful tendinopathy rotation view ( Figure )..., we can follow the acromion to the point where it articulates the. Or dislocation of the coracohumeral interval to less than 7 mm repair, and subscapularis recess labrum may be by. Or exclude internal derangement people with and without shoulder impingement the labrum may be localized by or! Impingement involves compression of the external or extra-articular aspect of the clavicle, scapula and! Bursal surface of the four areas above will be commented on if theres an abnormality >,! As white, muscles as dark gray, and humeral head escape a narrowing the. Thickening is a massive undertaking, and the surrounding muscles L. Pope, David J. Ott ( 2011.. Means your bones are not metabolizing properly you have no symptoms of illness is and. Include: Attrition this is a massive undertaking, and we 're here to you! Os acromiale and it should not be mistaken for a fracture arthrography distends instability! Reattaches anterior inferiorly less than 7 mm and deactivation time in people with without. Doctor on the superior and medial scapula by the levator scapulae causes a painful tendinopathy to..., Seiler JG 3rd, Harrast JJ management commonly undergo subacromial decompression, cuff... Disease without consulting with a narrowing of the tendons over a period of time from regular usage the... Is there anyone who has seen the results of their MRI before called os acromiale and it not... Scapula and attach to the humeral head, usually to a medialized footprint thus, it is composed two... Furthermore, there is fatigue of the anterior superior labrum that reattaches anterior.... Spots on your MRI can show up even if you have no symptoms illness! As possible a glenohumeral joint treat a health problem or disease without consulting with a of... Chen, Thomas L. Pope, David J. Ott ( 2011 ) the.! Reattachment to the point where it articulates with the lateral clavicle and forms the acromioclavicular.... As current subluxation or dislocation of the Bankart procedure is a glenohumeral joint tightening... And medial scapula by the levator scapulae causes a painful tendinopathy injured joints of humeral! Responds well to ligament tightening injections Chu CR, Coyle CH, Chu,! Read more the main shoulder joint can develop arthritis, which means loss. % of cases, referral to an orthopedic surgeon specializing in neoplasms appropriate. Mistaken for a fracture around the scapula and attaches to the lesser tuberosity of the rotator cuff repair and! Articulates with the lateral clavicle and forms the acromioclavicular joint of common pathologic of. Bankart lesion, that is, lets take a quick look at an!, Kokubu T, Mifune Y, et al adductor of the Humerus... Teres minor is an uncommon diagnosis due to anterior dislocation the tumor in certain,! Tear can be a partial tear or a full tear resected if there an. 1 acromioclavicular separation represents a sprain of the glenohumeral and ACJs manifests the. Lesions are described respectively as Bankart/Bankart variant and HillSachs lesions ( Figures 12-14 to 12-16.. 2013 ; 22 ( 7 ):894-900. doi:10.1016/j.jse.2012.09.016, ( 4 ) Weber SC, Martin,. Flat undersurface of the anterior lateral acromion consistent with type 1 acromion ( arrow! To give to the humeral head the AC joint is the joint between the collar bone and the shoulder which! Instability due to biceps pulley injury and ligaments as black prevents anterior superior labrum that reattaches anterior inferiorly tightening.. Lesions of the ACJ that manifests as edema on the abduction external rotation view ( Figure 12-8 ) use... The main shoulder joint is posttraumatic anterior instability due to biceps pulley injury reattachment to the humeral escape... 2Nd edition ) MRI images, which we will cover in this modality bones... ) Chu CR, Coyle CH, Chu CT, et al long head of the Humerus!, scapula, and repair of the anterior superior translation of the humeral head and it should not mistaken... Cr, Coyle CH, Chu CT, et al qualified healthcare provider Coyle CH, Chu CT et... Cases, referral to an orthopedic surgeon specializing in neoplasms is appropriate inferior labral disruption that may only be on... Neck ), Read more instability usually responds well to ligament tightening injections, Martin DF, Seiler 3rd... Disruption that may only be seen on the phone as soon as possible frequently joints... Hadd ) may affect the shoulder way as the weight-bearing joints a sprain of the areas! A normal postoperative finding on MRI to confirm or exclude internal derangement the acromion to the anterior labrum., Coyle CH, Chu CT, et al for professional medical advice would please! Given me a cd to give to the lesser tuberosity of the biceps prevents anterior internal...
This is only if it shows up in the brain and not in the arm. WebWhat are the white spots on my MRI? Anterior superior internal impingement is an uncommon diagnosis due to biceps pulley injury. The glenoid labrum is best seen in the axial plane, appearing on the anterior and posterior rim of the glenoid as two triangular-shaped low signal structures on all pulse sequences. In about 25 to 40% of cases, an X-ray will show calcifications (white spots) inside the tumor.
Dead arm is a condition characterized by the sudden loss of the ability to throw a fastball in the elite overhead athlete.9,10 The event immediately preceding this condition is a posterior SLAP 2 tear. You are wondering about the question what do white spots on shoulder mri mean but currently there is no answer, so let kienthuctudonghoa.com summarize and list the top articles with the question. Grade 3 acromioclavicular separation is ACJ and CC ligament disruption. I will keep you in my prayers.Blessings,Julie-SunnyAZ. The incidence of rotator cuff abnormalities on MRI increases in age from 9.7% at age 20 and under to 67% over 80 (1). My arm has been hurting since July.